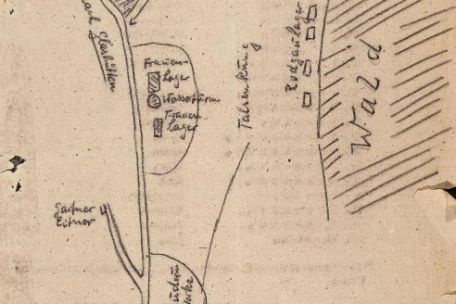
→ Forced Labor over the Course of the War
With the beginning of the war in September 1939, the first Polish civilians and prisoner of war were put to work in German agriculture. As the war expanded, the need for workers grew rapidly. For this reason, French prisoners of war were used as forced laborers beginning in 1940, and a year later also Serbian prisoners of war.
With the failure of the German blitzkrieg strategy against the Soviet Union in 1941, the lack of workers in the German Reich became more exacerbated. Hundreds of thousands of Soviet prisoners of war were forced into work. Concentration camp inmates became increasingly important to the war economy.
By 1942 the Germans were forcibly transporting more and more civilians from all over Europe into the German Reich. Rail transports arrived in the country on a daily basis. From their arrival points people were deployed to work sites and companies which had registered a need for workers with offices of the Labor Administration. A total of some 8.4 million civilian forced laborers were registered in Germany, among them an increasing number of women and minors.